Signalment
- 4 yo MN Abyssinian
History
- Never came home last night. Owner heard him meowing at the front door this morning and was breathing faster than normal and seemed painful when she picked him up. He didn’t want to eat when offered food.
Physical examination
- Heart rate: 188 bpm
- Pulse quality: Normal pulses, no deficits
- Respiratory: RR 66 bpm with increased inspiratory effort and reduced lung sounds on the right. There is crepitus when palpating the skin over the thorax and the cat seems painful.
- Circulatory: Pink moist mm crt <2sec
- Digestive: No abnormalities on abdominal palpation
- Urinary: A small bladder was palpated.
- Musculoskeletal: Ambulatory. Reluctant to walk. Nails scuffed.
Assessment
The history and clinical exam findings are suspicious of trauma. The tachypnea and dyspnea with reduced lung sounds is likely related to lung pathology. With the history and physical examination findings pulmonary pathology (such as pulmonary contusions, traumatic bullae, non cardiogenic oedema) or pleural space disease (haemorrhage, pneumothorax, pleuroperitoneal hernia) is a concern. Pain and stress should also be considered.
The crepitus overlying the skin could be due to cutaneous trauma or mediastinal disease such as a pneumomediastinum is possible.
The reluctance to walk could be due to the findings above or soft tissue or skeletal abnormalities such as fractures are likely.
Left lateral projection
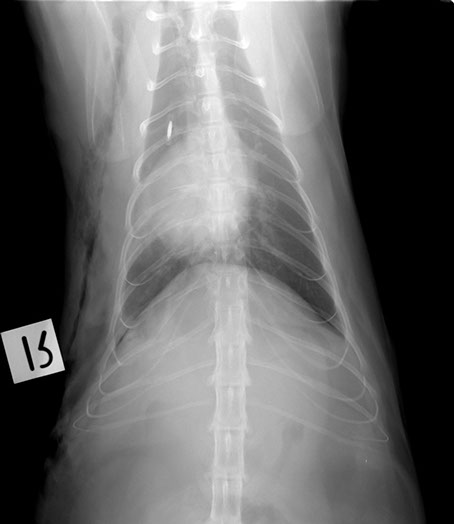
Dorso-ventral projection
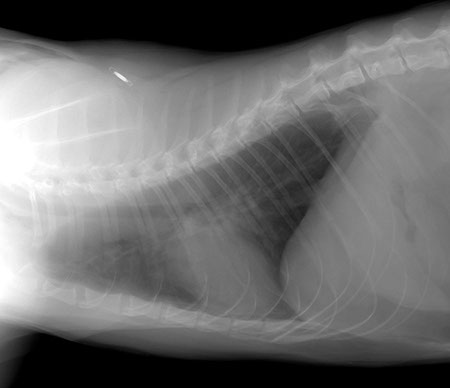
Right lateral projection
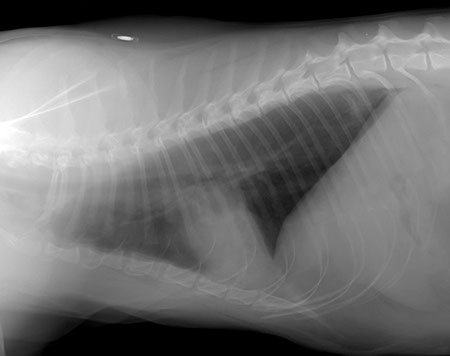
Oblique projection
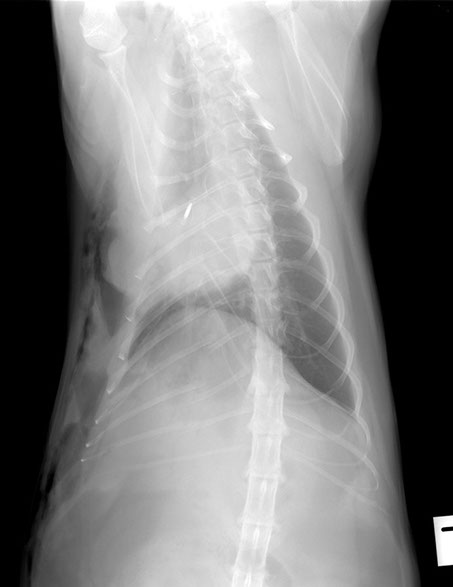
Radiographic findings
Widened interlobar soft tissue fissures
Lateral projection
DV projection
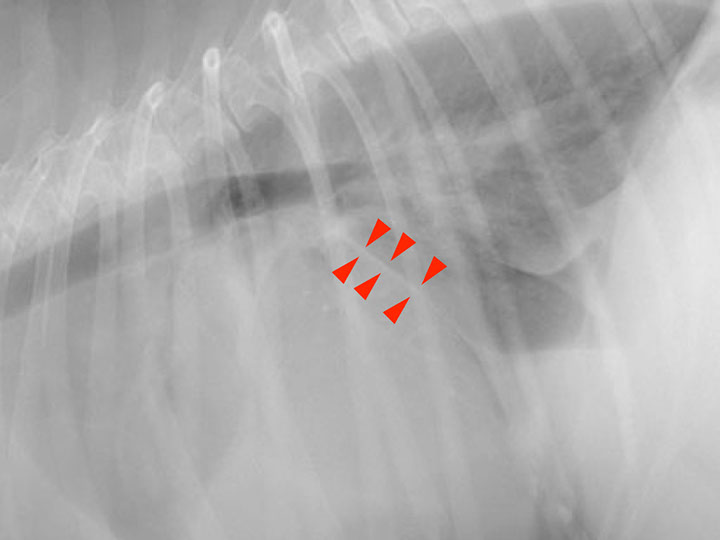
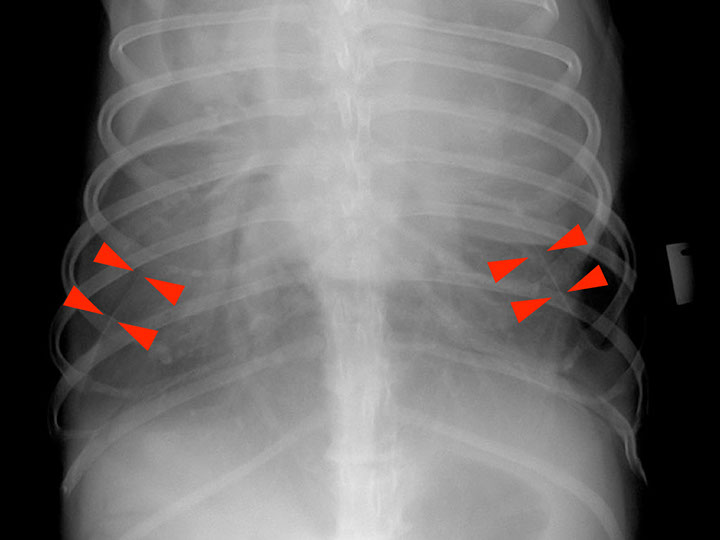
Interlobar pleural fissure lines are the result of accumulation of fluid (soft tissue opacity) between the lung lobes
Retraction of the lung away from the thoracic wall (interposed soft tissue opacity)
Lateral projection
DV projection
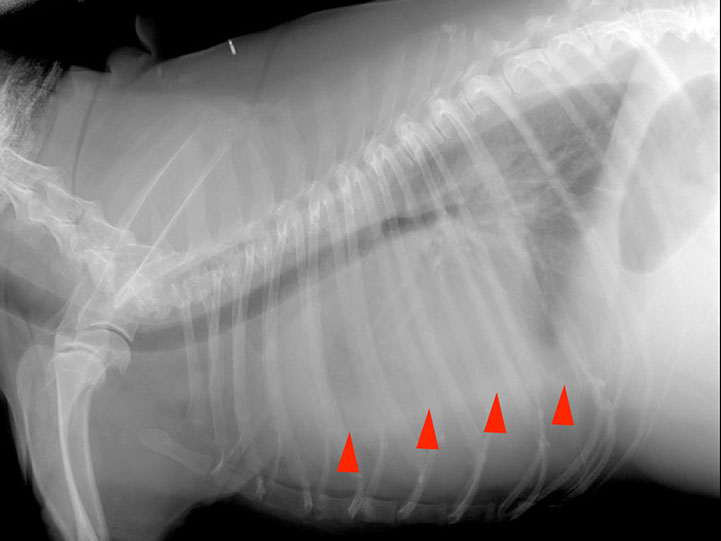
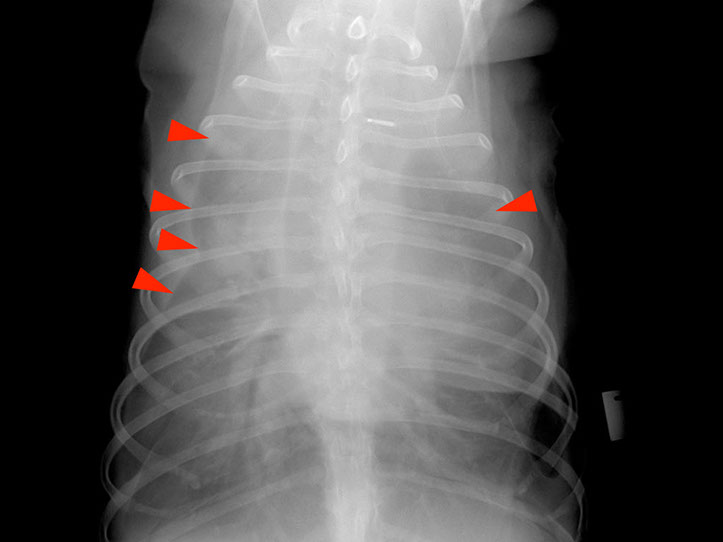
Retraction of the lungs is the consequence of accumulation of fluid in the pleural space
Obscured cardiac silhouette and diaphragm
Lateral projection
DV projection
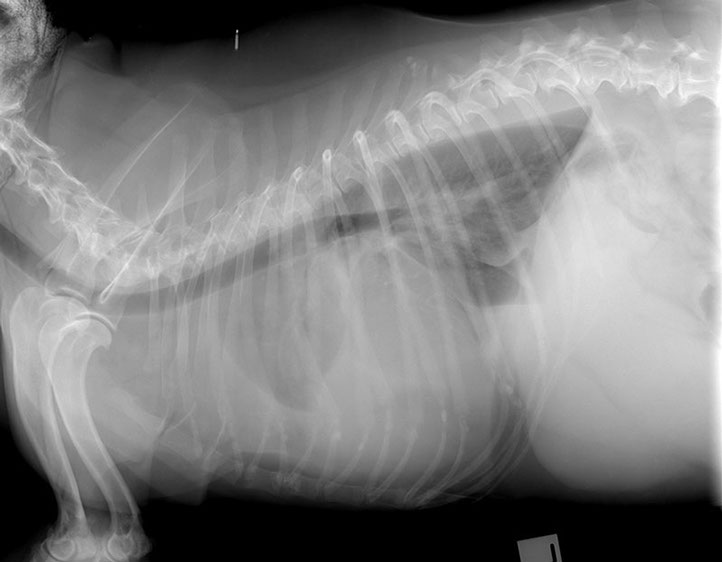
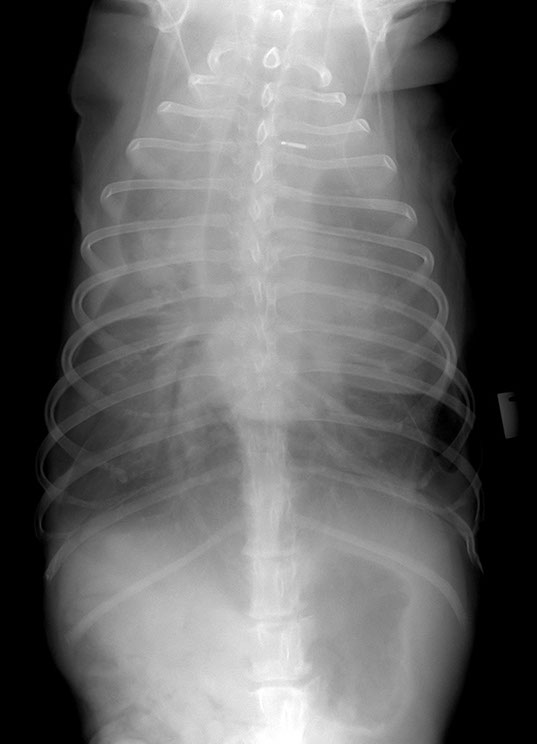
Note: remember that when 2 structures of the same opacity, such as peritoneal effusion and pericardium, are in contact their contours are obliterated. This is called border effacement or silhouette sign
Dr Mariano Makara
Dip. ECVDI